In recent years, there has been great popularity in the use of LED products. This is why mcpcbs – metal core printed circuit boards have also gained popularity. The lighting and automobile sectors have already accepted the technology, same way consumers have. This is because an LED light can prove to be five times less expensive compared to the incandescent unit. Also, compact fluorescents seem to have a little higher cost for operating and when we talk about using space efficiently, they don’t have what it takes to compete with very small LEDs.
Due to these, as well as other factors, many other devices have started incorporating LEDs as one very important design feature. However, there is a very important aspect of operation of LEDs, which has to be accounted for when handling product designs; that is heat.
What is a metal core PCB?
A metal core printed circuit board (MCPCB) also known as thermal PCB, incorporates a metal material as its base as opposed to the traditional FR4, for the heat spreader fragment of the board. Heat builds up due to some electronic components during the operation of the board. The purpose of the metal is to divert this heat away from critical board components and towards less crucial areas such as the metal heatsink backing or metallic core. Hence, these PCBs are apt for thermal management.
In a multilayer MCPCB, the layers will be evenly distributed on each side of the metal core. For instance, in a 12-layer board, the metal core will be at the center with 6 layers on the top and 6 layers at the bottom.
MCPCBs are also referred to as insulated metallic substrate (IMS), insulated metal PCBs (IMPCB), thermal clad PCBs, and metal-clad PCBs. In this article, we will be using the abbreviation MCPCB to avoid ambiguity.
The MCPCBs are made up of thermal insulating layers, metal plates, and metal copper foil.
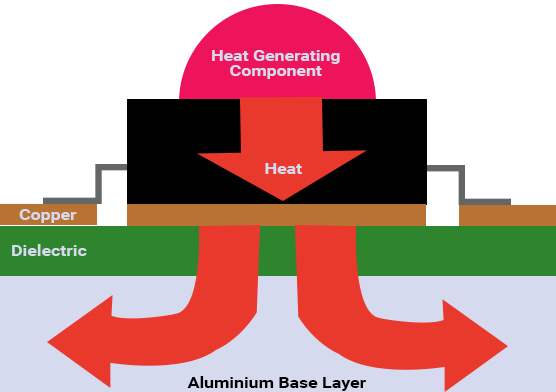
The basic structure of MCPCB comprises of the following:
- Solder mask
- Circuit layer
- Copper layer – 1oz. to 6oz. (most commonly used 1oz. to 2oz.)
- Dielectric layer
- Metal core layer – heat sink or heat spreader
Benefits of MCPCB
In so many scenarios, LEDs are similar to all other components that can be mounted on or attached to a circuit board. The fact is that if just a few LEDs are available like red and green indicators, then whenever you are laying out the PCB, the reason to do something unusual will be little. However, lighting solutions which integrate either arrays or rows of MCPCB LEDs are available. This stays on for a long time period.
Ensuring that these devices are kept cool to prevent them from failing prematurely, as well as creating a safety hazard could become a major problem. Cooling it efficiently is also necessary to ensure that there is a consistent light output. Converting your PCB to a MCPCB from the standard type (FR4)is also a good alternative to consider.
Some benefits of metal core PCBs is its use of unique substrate materials that are formulated specifically to help in improving the designs’ reliability, which run at temperatures that are above normal
Rather than serve as just a surface for mounting for these components, these substrates help in drawing heat actively from areas where the components are hot-running via the mcpcb board’s opposite layer, where dissipation can be done safely and efficiently.
MCPCB has proved to be a great solution to problems concerning the cooling of PCBs using a large number of LEDs.
