The meanings and differences of VCC, VEE, VDD, and VSS used in the supply voltage are shown below.
-
VCC
- VCC is used as the positive supply voltage for circuits using a bipolar transistor (BJT).
- The "C" in "VCC" stands for Collector.
- It is widely believed that the reason for repeating "VCC" and "C" twice is to distinguish it from the collector voltage VC.
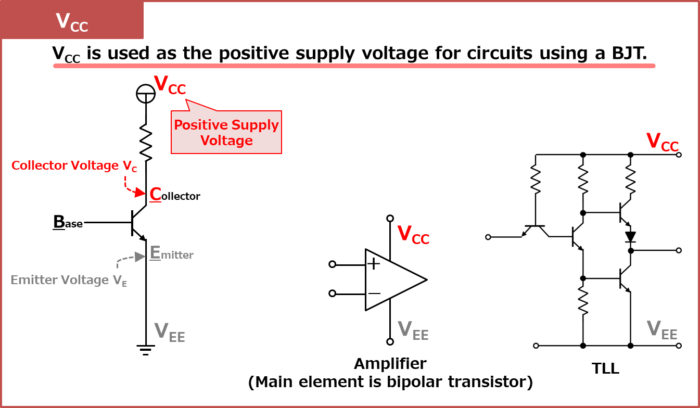
VCC is used as the positive supply voltage for circuits using a bipolar transistor (BJT).
The positive supply voltage on the collector side of the NPN bipolar transistor is "VCC". The collector terminal of an NPN bipolar transistor is often connected directly to VCC or VCC through a resistor or other means.
The "C" in "VCC" stands for Collector. It is widely believed that the reason for repeating "VCC" and "C" twice is to distinguish it from the collector voltage VC.
Circuits that use multiple positive supply voltages are often represented by different supply voltages, such as "VCC1, VCC2, …".
VCC is also used as the positive supply voltage for operational amplifiers, whose main elements that make up the internal circuit are bipolar transistors, and for TLL (Transistor-transistor logic).
Supplement
"V+" and "V-" also represent the power supply voltage.
Therefore, "V+" may be used instead of "VCC" for the positive supply voltage of circuits using a bipolar transistor (BJT).
-
VEE
- VEE is used as a negative supply voltage for circuits that use a bipolar transistor (BJT).
- The "E" in "VEE" stands for Emitter.
- It is widely believed that the reason for repeating "VEE" and "E" twice is to distinguish it from the emitter voltage VE.

VEE is used as a negative supply voltage for circuits that use a bipolar transistor (BJT).
The negative supply voltage on the emitter side of the NPN bipolar transistor is "VEE". The emitter terminal of an NPN bipolar transistor is often connected directly to VEE or VEE through a resistor or other means. In the case of a single power supply system, "VEE" is at the same potential as the ground.
The "E" in "VEE" stands for Emitter. It is widely believed that the reason for repeating "VEE" and "E" twice is to distinguish it from the emitter voltage VE.
Circuits that use multiple negative supply voltages are often represented by different supply voltages, such as "VEE1, VEE2, …".
VEE is also used as the negative supply voltage for operational amplifiers, whose main elements that make up the internal circuit are bipolar transistors, and for TLL (Transistor-transistor logic).
Supplement
"V+" and "V-" also represent the power supply voltage.
Therefore, "V-" may be used instead of "VEE" for the negative supply voltage of circuits using a bipolar transistor (BJT).
-
VDD
- VDD is used as the positive supply voltage for circuits that use a field-effect transistor (FET).
- The "D" in "VDD" stands for Drain.
- It is widely believed that the reason for repeating "VDD" and "D" twice is to distinguish it from the drain voltage VD.
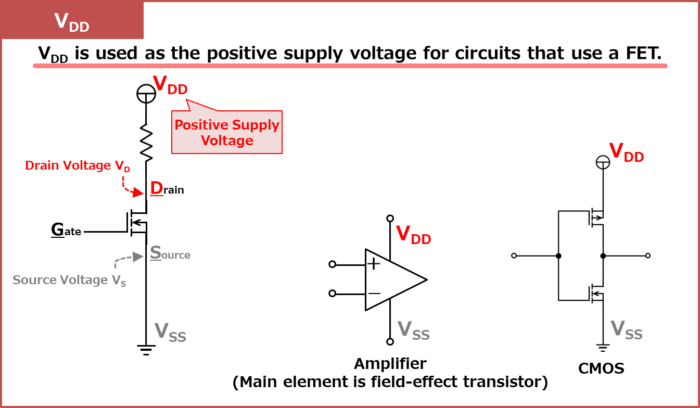
VDD is used as the positive supply voltage for circuits that use a field-effect transistor (FET).
The positive supply voltage on the drain side of the N-channel field-effect transistor (NchFET) is "VDD". The drain terminal of an N-channel field-effect transistor (NchFET) is often connected directly to VDD or VDD through a resistor or other means.
The "D" in "VDD" stands for Drain. It is widely believed that the reason for repeating "VDD" and "D" twice is to distinguish it from the drain voltage VD.
Circuits that use multiple positive supply voltages are often represented by different supply voltages, such as "VDD1, VDD2, …".
VDD is also used as the positive supply voltage for operational amplifiers, whose main elements that make up the internal circuit are field-effect transistors, and for CMOS(Complementary MOS).
Supplement
"V+" and "V-" also represent the power supply voltage.
Therefore, "V+" may be used instead of "VDD" for the positive supply voltage of circuits using a field-effect transistor (FET).
-
VSS
- VSS is used as the negative supply voltage for circuits that use a field-effect transistor (FET).
- The "S" in "VSS" stands for Source.
- It is widely believed that the reason for repeating "VSS" and "S" twice is to distinguish it from the source voltage VS.
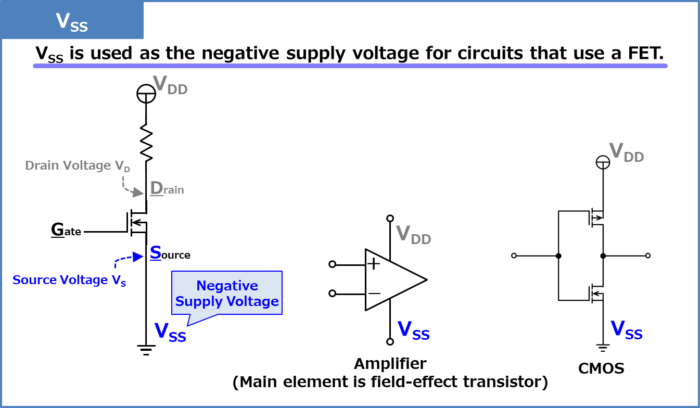
VSS is used as the negative supply voltage for circuits that use a field-effect transistor (FET).
The negative supply voltage on the source side of the N-channel field-effect transistor (NchFET) is "VSS". The source terminal of an N-channel field-effect transistor (NchFET) is often connected directly to VSS or VSS through a resistor or other means. In the case of a single power supply system, "VSS" is at the same potential as the ground.
The "S" in "VSS" stands for Source. It is widely believed that the reason for repeating "VSS" and "S" twice is to distinguish it from the source voltage VS.
Circuits that use multiple negative supply voltages are often represented by different supply voltages, such as "VSS1, VSS2, …".
VSS is also used as the negative supply voltage for operational amplifiers, whose main elements that make up the internal circuit are field-effect transistors, and for CMOS(Complementary MOS).
Supplement
"V+" and "V-" also represent the power supply voltage.
Therefore, "V-" may be used instead of "VSS" for the negative supply voltage of circuits using a field-effect transistor (FET).
