What Is Wire Bonding?
Wire bonding is a versatile interconnect technology that involves using thin wires, is a crucial process in semiconductor device fabrication that involves creating electrical connections between a silicon chip and its external leads using very fine bonding wires made of materials such as copper, gold, and aluminum. These wire bonds provide a pathway for the transfer of electrical signals, power, and ground between different parts of the circuit.
Here is a simple example of a bonding wire size chart:
| Bonding Wire Diameter | Diameter (μm) | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 0.7 mil | 17.8 | Micro-bonding |
| 1.0 mil | 25.4 | General-purpose |
| 1.2 mil | 30.5 | Standard applications |
| 1.5 mil | 38.1 | High-power bonding |
| 2.0 mil | 50.8 | High-power applications |
| 2.5 mil | 63.5 | Special applications |
| 3.0 mil | 76.2 | Special applications |
Therefore, wire bonding is a critical process in semiconductor device fabrication that involves creating electrical connections between the chip and its external leads using fine bonding wires made of materials like copper, gold, and aluminum. Wire bonding machines and precious tools such as capillaries and wire clamps play a crucial role in this process, and their proper selection is essential for achieving consistent and reliable bonding results.
Apply wire bonding to PCB connections.
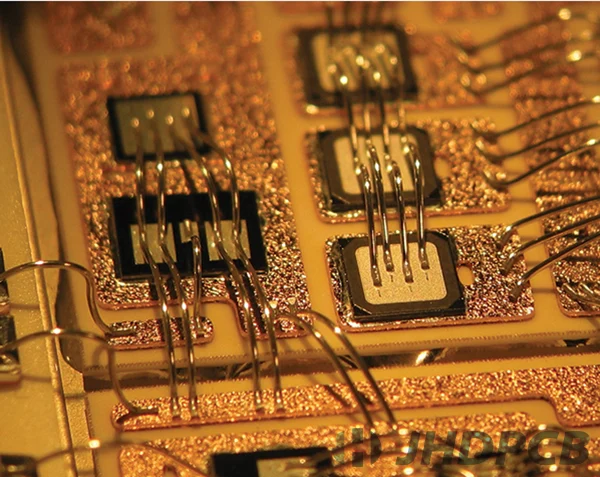
Wire bonding and printed circuit boards (PCBs) are two different processes used in the assembly of semiconductor devices. However, wire bonding is often used to make connections between a semiconductor device and a PCB.
When a semiconductor device is manufactured, it is typically mounted onto a substrate or package using wire bonding. The wire bonds are then connected to the PCB using a variety of methods, including soldering, flip-chip bonding, or conductive adhesive.
In some cases, the PCB itself may be manufactured using wire bonding techniques. For example, some flip-chip packages use wire bonding to connect the semiconductor die to the package substrate. In such scenarios, the wire bonds act as the electrical links connecting the die to the substrate, which is essentially a tiny printed circuit board (PCB).
Overall, wire bonding and PCBs are both important processes in the assembly and manufacturing of semiconductor devices. While they are distinct processes, they often work together to create reliable and high-quality electronic components.
Flip Chip Vs Wire Bond.
Flip chip and wire bonding are two commonly used methods in microelectronics for creating electrical connections between integrated circuits (ICs) or semiconductor devices and their respective packaging or substrates.
Wire bonding is a process that uses thin wires, typically made of gold or aluminum, to create conductive paths between the bonding pad on the IC and the package or substrate. The wire is bonded to the pad using heat and pressure, creating a permanent connection.
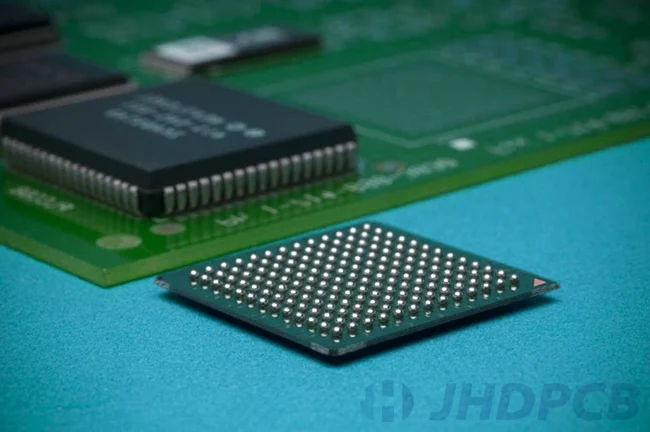

Flip chip, on the other hand, involves flipping the IC and placing its contacts directly onto the substrate or package. The contacts are typically made of solder bumps or copper pillars, which form the electrical connection when they melt and bond during reflow.
In comparison, flip chip typically offers better electrical performance due to shorter interconnect lengths and higher input/output density. It also allows for higher integration levels, enabling more components to be packed into a smaller area. Wire bonding, on the other hand, is generally less expensive, easier to implement, and more flexible in terms of design and customization.
Both flip chip and wire bonding have their respective advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which one to use depends on factors such as cost, performance requirements, design complexity, and production volume.
What Are The Materials Used In Wire Bonding?
Good conductivity, weldability, hardness, and corrosion resistance are necessary for wire bonding materials.Following are the materials and their combinations:
|
Material |
Properties | Alloy Combinations | Bonding Techniques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum (Al) | Thermal and electrical conductivity, low cost, good workability | Al-Au, Al-Ni, Al-Si, Al-Mg | Thermosonic bonding |
| Copper (Cu) | Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, higher strength than Al | – | Ball bonding with ultrasonic energy |
| Silver (Ag) | Good thermal and electrical conductivity, low resistivity, high ductility | Ag-Au, Ag-Al, Ag-SiC | Bonding with ultrasonic energy |
| Gold (Au) | Excellent electrical conductivity, ductility, compatibility with silicon chip | Au-Al, Au-Cu, Au-Pd |
Thermocompression bonding, thermosonic bonding |
