Difference between VCC and VDD
In microcontrollers, VCC is the most common power supply pin, usually used to provide the forward voltage required in digital circuits. The voltage of VCC is usually 3.3V or 5V, but there are microcontrollers with other voltage levels.
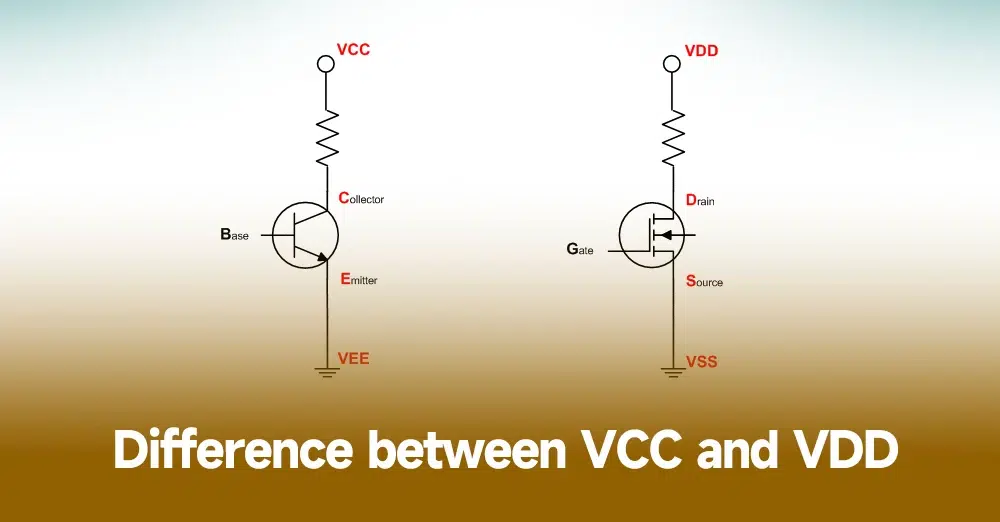
And VDD is a special type of power supply voltage, which refers to the power supply voltage used in CMOS circuits. In CMOS circuits, the transistors used are MOSFETs, which require two types of voltages to work: forward voltage and reverse voltage. VDD refers to the forward voltage required for MOSFET operation, and its voltage is usually lower than VCC, usually between 1.8V and 3.3V.
In use, the difference between VCC and VDD is mainly in the circuit type and voltage level. VCC is suitable for common digital circuits, while VDD is mainly suitable for CMOS circuits. This is because MOSFET transistors in CMOS circuits require two voltages: a forward voltage and a reverse voltage. In digital circuits, usually only one forward voltage is needed, so VCC is usually used to provide the forward voltage.
Application of VCC and VDD in MCU
In the single-chip microcomputer, the application of VCC and VDD is basically the same as that in other digital circuits. VCC and VDD are used to provide the power supply voltage required for the operation of the single-chip microcomputer to ensure that the single-chip microcomputer can work normally. In addition, other pins of the microcontroller also need to be connected to VCC and VDD to ensure that they can work normally.
In the design of single-chip microcomputer, in order to avoid the instability of the circuit, it is usually necessary to connect ceramic capacitors to VCC and VDD. These capacitors help filter out high-frequency noise in the power supply, thereby increasing the stability and reliability of the circuit. It should be noted that these capacitors need to choose the appropriate capacitance value and capacitance to ensure that they can filter the desired noise.
In some microcontrollers, VCC and VDD may be used for different functions. For example, some microcontrollers may need to use VCC to provide internal logic voltage and VDD to provide analog circuit voltage. Therefore, when using a microcontroller, we need to consult the corresponding data sheet to determine the specific usage and voltage requirements of VCC and VDD.
In addition, in the design and application of the single-chip microcomputer, some issues related to the power supply voltage need to be paid attention to. For example, the voltage range of VCC and VDD must be within the specification requirements of the microcontroller, otherwise it may cause the microcontroller to malfunction or be damaged. In addition, in the circuit design, attention should be paid to the stability of the power supply voltage and noise filtering to ensure the stability and reliability of the single-chip microcomputer.
In practical applications, the connection mode of VCC and VDD also needs to be determined according to the specific circuit design. Normally, VCC and VDD can be directly connected to the supply voltage, or connected after being regulated by a voltage regulator. When connecting, pay attention to the location of the connection and the polarity of the power supply voltage to avoid problems caused by wrong connections.
