The RF module consists of a 433 MHz RF transmitter and receiver modules. These are ASK (Amplitude shift keying) or OOK (Of Hook Keying) type RF modules. While transmitting logic zero the transmitter fully suppresses the carrier frequency and hence consumes only low power in battery operation. When logic one is transmitted the transmitter is ON, and the carrier frequency is full and hence, there will be a high power supply that is in the range of about 4.5mA with a 3V power supply.
The transmitter and receiver are needed to be interfaced with microcontrollers for data transfer. The data is sent serially from the transmitter and is received by a tuned receiver. The RF transmitter receives serial data from a microcontroller and transmits it to the receiver through an antenna connected to the 4th pin of the transmitter. The receiver receives the data through an antenna and gives the data to the microcontroller connected to it.
These RF modules operate at a specific frequency of 433MHz. RF signals can travel between transmitter and receiver even when there is an obstruction. These modules are used for short range, low- budget, simplex-based communication. The low power consumption makes them ideal for battery- based implementations. It is used in various areas like Remote lighting controls, long-range RFID, wireless alarm and security systems etc. RF communication is used in Mobile communication and can have long rage communication and that’s what make them suitable for building IoT based applications. So here we are starting with a introductory Article about RF modules and how RF modules can be used with Arduino to send and receive data.
433 MHz RF Transmitter Module
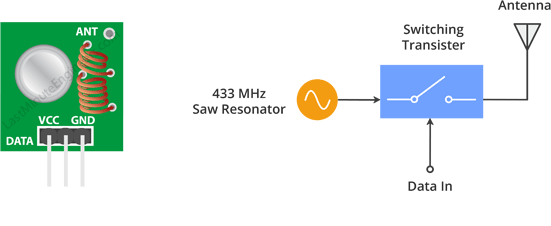
This small module is the RF transmitter. It is very simple. The SAW resonator which is tuned for 433.xx MHz operation is the heart of the module. There is a switching transistor and a few passive components on it.
When a logic HIGH is given as the DATA input, the oscillator is ON and produces a constant RF output carrier wave at 433.xx MHz and when the DATA input is logic LOW, the oscillator is OFF, so no carrier is produced. This technique is called Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK).
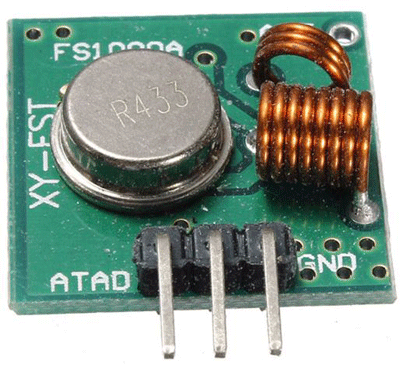
Specifications
- Working voltage: 3V – 12V
- Working current: max Less than 40mA, and min 9mA
- Resonance mode: (SAW)
- Modulation mode: ASK
- Working frequency: 433.92MHz
- Transmission power: 25mW
- Frequency error: +150kHz (max)
- Velocity: less than 10Kbps
- Transmission range: 90m (in open space)
433 MHz RF Receiver Module

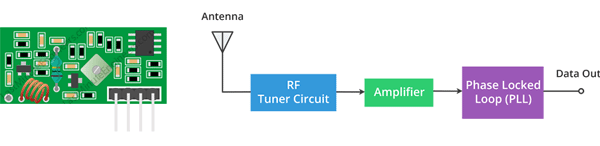
This is the RF receiver module. Even though it looks complex, it is as simple as the transmitter module. It consists of an RF tuner circuit, OP Amps, and a PLL. A couple of OP-Amps are used to amplify the carrier wave received from the transmitter. The amplified signal is then fed to a PLL (Phase Lock Loop) which enables the decoder to “lock” onto a stream of digital bits which gives better-decoded output and noise immunity.
Specifications
- Working voltage: 5.0VDC +0.5V
- Working current:≤5.5mA max
- Modulation mode: OOK/ASK
- Working frequency: 433.92MHz
- Bandwidth: 2MHz
- Sensitivity: exceeds –100dBm (50Ω)
Specifications
- Working voltage: 5.0VDC +0.5V
- Working current:≤5.5mA max
- Modulation mode: OOK/ASK
- Working frequency: 433.92MHz
- Bandwidth: 2MHz
- Sensitivity: exceeds –100dBm (50Ω)
Required Components
- Arduino Nano (2)
- RF 433MHz Transmitter Module
- RF 433MHz receiver module
- Potentiometer
- LED (5)
- Connecting wires
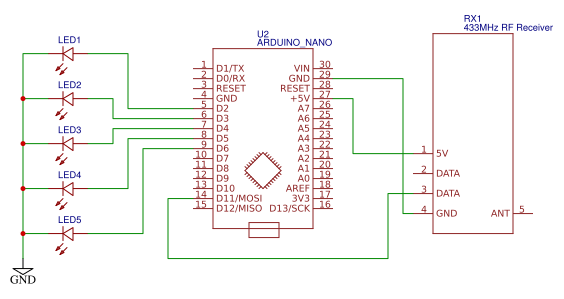
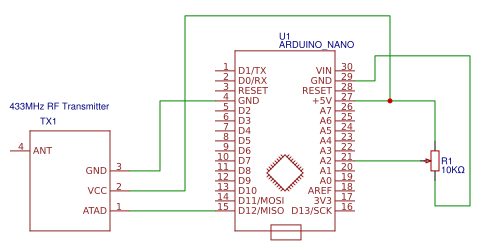
Circuit Diagram
The circuit diagram for RF transmitter using Arduino Nano is given below. Here a potentiometer is connected to vary the values to be sent to receiver using the RF transmitter.
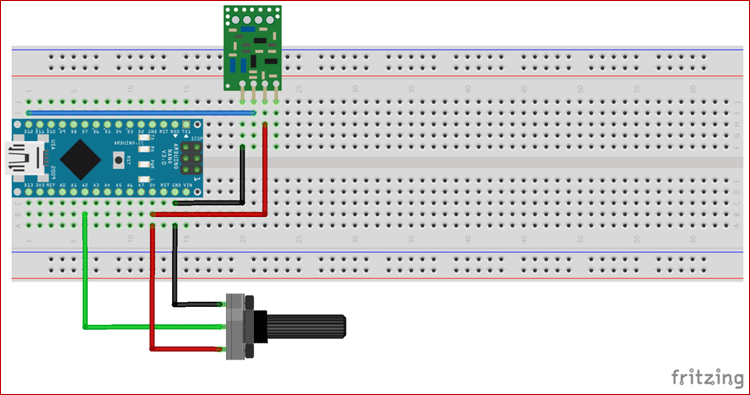
Below are the Pin connections details between RF transmitter and Arduino
- D12 pin of Arduino – DATA pin of RF transmitter
- VCC of Arduino – VCC of RF transmitter
- GND of Arduino – GND of RF transmitter
- GND of Arduino – first pin of the potentiometer
- A2 pin of Arduino – Second pin of the potentiometer
- VCC of Arduino – third pin of the potentiometer

The circuit diagram for RF receiver using Arduino Nano is shown below. Here we have a series of LEDs. The LEDs are shifted based on the potentiometer values received by the receiver.


Below are the Pin connections details between RF receiver and Arduino
- D11 pin of Arduino - DATA pin of RF receiver.
- VCC of Arduino - VCC of RF receiver.
- GND of Arduino - GND of RF receiver.
- Positive leads of LEDs are connected to the digital pins D2, D3, D4, D5, and D6
- Negative leads of the LEDs are grounded.