HOW TO CHOOSE A SOLAR PANEL
To power a Raspberry Pi, the solar panel needs to output at least 5V. The wattage and current ratings of the solar panel will determine how fast the battery charges. This means a 2W solar panel can charge a battery twice as fast as a 1W solar panel.
THE BATTERY CHARGE CONTROLLER
The voltage and current output by the solar panel will vary greatly depending on the amount of light hitting it. These voltage and current fluctuations could damage the Raspberry Pi.
A battery charge controller will prevent this from happening by supplying a constant voltage and current to the Raspberry Pi, while at the same time providing the correct voltage and current to safely charge the battery.
TP4056 CHARGE CONTROLLER
This setup uses a TP4056 charge controller to power the Raspberry Pi and charge a 3.7V lithium battery. The TP4056 charge controller’s input pins are connected to the output of the solar panel. The OUT+ and OUT- pins are connected to the 5V and ground pins on the Raspberry Pi, and the B+ and B- pins are connected to the battery:
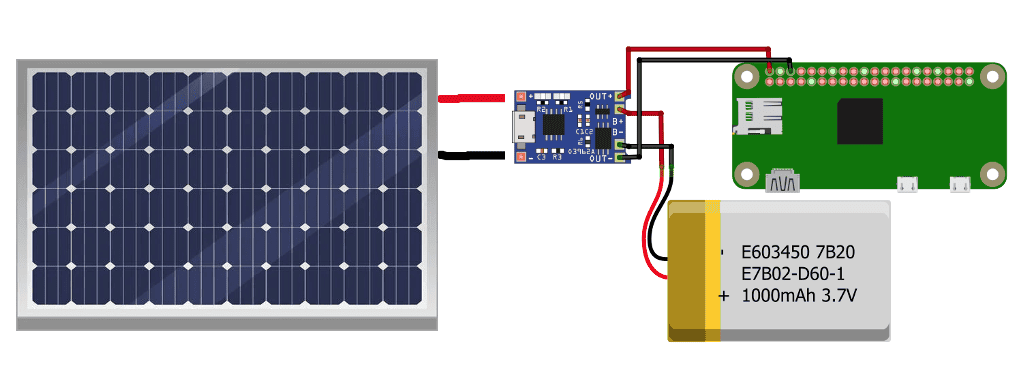
This setup has one problem though. The TP4056 charger controller only outputs 3.7V. To power the Raspberry Pi effectively, we need a 5V power supply.
TP4056 AND A DC/DC CONVERTER
The solution to this is to use a DC/DC converter to increase the 3.7V to 5V. All we need to do is insert a 3.7V to 5V DC/DC converter between the output of the charge controller and the Raspberry Pi’s power pins like this:
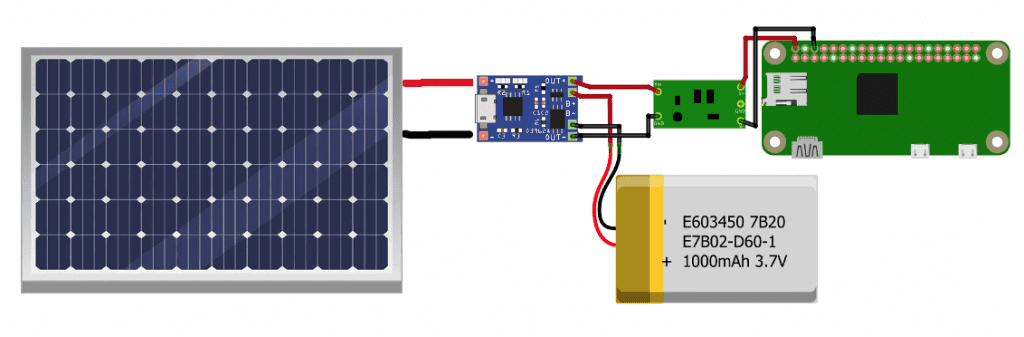
With this setup, you can be sure your Raspberry Pi will be operating at the correct voltage.
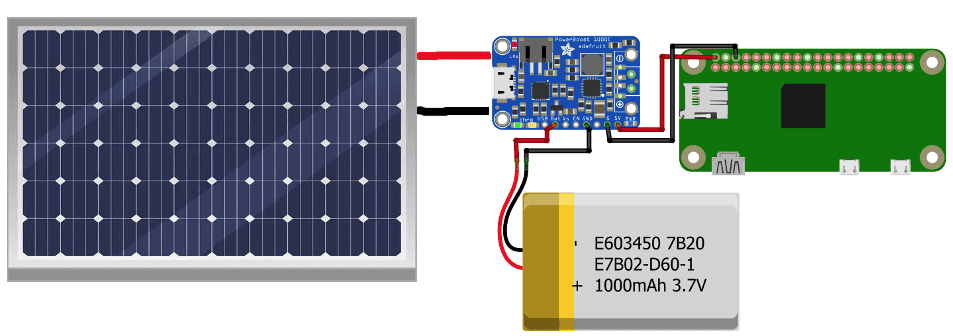
ADAFRUIT’S POWERBOOST MODULE
This setup uses the PowerBoost 1000 charge controller from Adafruit. This module works like a battery charge controller and a DC/DC converter in one. With this module there is there is no need for a separate charge controller and DC/DC converter – they are all contained in one module.
This circuit will provide a constant 5V to the Raspberry Pi and supply the battery with the correct current and voltage for a safe charge: